Hydration is a cornerstone of health, intricately linked to the body’s optimal performance across various physiological processes. Ignoring the body’s hydration needs can lead to dehydration, a condition that can subtly undermine health before one is fully aware of its impact. Recognizing the signs of dehydration is crucial, as it affects more than just thirst; it impacts energy levels, cognitive function, and even emotional well-being. This article delves into eight signs of dehydration that should not be ignored, offering insights into each symptom’s implications and the underlying mechanisms.
Contents
Excessive Thirst
Excessive thirst is the body’s alarm bell, signaling it’s time to replenish fluid levels. This sensation is a direct result of the body’s attempt to balance its fluid levels, triggered by a decrease in blood volume and an increase in the concentration of solutes in the bloodstream. When these changes are detected, the brain sends a thirst response to encourage water intake. Ignoring this crucial signal can lead to further dehydration, exacerbating the body’s fluid imbalance and potentially leading to more severe health issues. Understanding and responding to this basic need is the first step in preventing dehydration and maintaining health.
The relationship between thirst and hydration is often overlooked in daily routines, especially in busy or stressful environments. Yet, staying attuned to this fundamental signal is essential for preventing dehydration. Regular water intake is vital, particularly for individuals engaged in physical activity or those exposed to hot climates, as these conditions can increase fluid loss through sweat. Encouraging the habit of carrying a water bottle and drinking regularly throughout the day can help prevent the onset of dehydration and its accompanying symptoms, ensuring the body remains well-hydrated and functional.
Dry Mouth and Bad Breath

A dry mouth is more than just uncomfortable; it’s a telltale sign of dehydration. Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health; its production diminishes when the body is dehydrated. This reduction can lead to the uncomfortable feeling of dryness in the mouth, often accompanied by bad breath. Saliva contains antimicrobial agents that help control the growth of bacteria. When its production decreases, bacteria can proliferate, leading to increased bad breath. This symptom serves as a reminder of the body’s need for water, underscoring the importance of regular hydration.
Moreover, addressing dry mouth and bad breath requires more than just temporary solutions like mints or gum; it necessitates a commitment to regular water intake. Keeping the body adequately hydrated ensures that saliva production remains at a level that supports oral hygiene and health. It’s also beneficial to avoid beverages that can exacerbate dehydration, such as those containing caffeine or alcohol. By prioritizing hydration, individuals can alleviate the discomfort of dry mouth and mitigate the occurrence of bad breath, contributing to both oral health and overall well-being.
Fatigue and Weakness

Fatigue and weakness are often misattributed to lack of sleep or overexertion, yet they are frequently indicators of dehydration. When the body lacks sufficient fluids, blood volume can decrease, reducing the amount of oxygen and nutrients that reach the muscles and organs. This scarcity can result in feelings of tiredness and a lack of energy, even without engaging in physically demanding activities. The link between dehydration and fatigue underscores the importance of regular fluid intake as part of a healthy lifestyle.
Furthermore, chronic dehydration can exacerbate feelings of weakness, making daily tasks seem more challenging and affecting the overall quality of life. It’s essential to recognize these signs early and address them by increasing water consumption. For individuals who find plain water unappealing, incorporating flavored waters or eating high-water-content fruits and vegetables can be an effective way to enhance hydration. Staying vigilant about fluid intake can significantly impact energy levels and physical performance, illustrating the connection between hydration and vitality.
Headaches and Dizziness

Headaches and dizziness are common complaints that can stem from various causes but are also significant indicators of dehydration. Dehydration can cause the brain to temporarily contract or shrink from fluid loss. This mechanism can lead to pain and is often perceived as a headache. The body’s attempt to maintain fluid balance by constricting blood vessels can also contribute to feelings of dizziness or lightheadedness. Recognizing these symptoms as potential signs of dehydration is crucial for timely intervention and preventing more severe dehydration effects.
Addressing dehydration-induced headaches and dizziness involves more than reaching for pain relief; it requires replenishing the body’s fluid levels. Drinking water at the first sign of these symptoms can provide quick relief by restoring fluid balance and aiding in the brain’s and circulatory system’s normal functioning. Establishing a routine of consistent water intake throughout the day can help prevent these symptoms, demonstrating the importance of hydration in maintaining cognitive and physical health.
Dark Urine and Reduced Urination

One of the most straightforward indicators of hydration status is the color and frequency of urination. Dark urine and reduced urination are clear signs that the body conserves water due to inadequate fluid intake. Under normal hydration conditions, urine should be light yellow, indicating that the body is expelling waste effectively without conserving water. Darker urine suggests that the kidneys are retaining fluid to maintain bodily functions, signaling the need for increased water intake.
Monitoring urine color and frequency can be a practical guide for staying hydrated. Changes in these factors can provide immediate feedback on the body’s hydration status, prompting adjustments in water consumption. Aiming for regular, light-colored urination as a sign of proper hydration is advisable. Encouraging the intake of fluids throughout the day, especially before, during, and after physical activity or in hot weather, can help maintain optimal hydration levels and support kidney function, emphasizing the role of hydration in overall health maintenance.
Dry Skin and Lips
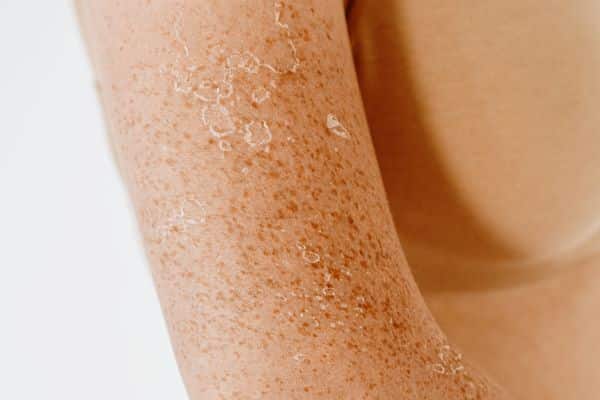
The impact of dehydration extends beyond internal symptoms, manifesting visibly in the condition of the skin and lips. Dry, flaky skin and chapped lips are external signs of the body’s lack of moisture, highlighting the need for adequate hydration. The skin, the body’s largest organ, requires significant water to remain healthy, elastic, and vibrant. When hydration levels drop, the skin loses its plumpness and elasticity, leading to dryness and signs of aging. Similarly, the lips are sensitive to changes in hydration levels, with dryness and chapping directly responding to inadequate water intake.
Maintaining skin and lip health involves more than topical moisturizers and lip balms; it necessitates proper hydration from within. Drinking sufficient water ensures that the skin and lips receive the moisture they need to stay healthy and resilient. Additionally, incorporating hydrating skincare routines, such as using hydrating serums or masks, can support the skin’s moisture barrier and complement the benefits of drinking water. This holistic approach to hydration emphasizes the interconnectedness of internal and external health, showcasing the wide-reaching benefits of maintaining adequate hydration levels.
Given the character limit, let’s continue with the remaining headings and conclusion in a follow-up response.
Rapid Heart Rate and Breathing

Dehydration can significantly affect the cardiovascular system, increasing heart rate and rapid breathing. When the body is dehydrated, there is less plasma in the blood, which can cause the heart to work harder to pump blood to the organs, resulting in an elevated heart rate. Similarly, dehydration can lead to a quicker breathing rate as the body tries to cool itself down and maintain oxygen levels with less blood volume. These symptoms can be particularly alarming, as they mimic the signs of other serious health conditions, highlighting the critical need for prompt hydration to avoid further complications.
Furthermore, recognizing the signs of rapid heart rate and breathing as potential indicators of dehydration allows for timely interventions to prevent the escalation of symptoms. Individuals must listen to their bodies and respond to these signals by increasing fluid intake, especially during hot weather or physical activity. Keeping hydrated can help stabilize the heart rate and breathing, ensuring the body operates efficiently and reducing the risk of dehydration-related stress on the cardiovascular system.
Irritability and Confusion

The brain’s function is heavily influenced by hydration status, with dehydration potentially leading to irritability and confusion. These mental and emotional changes directly result from the brain’s sensitivity to fluid imbalances, affecting mood, cognitive function, and decision-making abilities. Dehydration can disrupt the delicate balance of electrolytes, essential for transmitting signals between brain cells. This disruption can result in irritability, difficulty concentrating, and confusion, impacting an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks effectively.
Addressing these symptoms requires recognizing the importance of hydration in maintaining mental clarity and emotional stability. Regular water intake can significantly reduce the risk of experiencing dehydration-related cognitive impairments. Additionally, it is beneficial to be mindful of situations that might increase fluid loss, such as high temperatures or intense exercise, and adjust water consumption accordingly. By prioritizing hydration, individuals can support their brain health, enhance their mood, and improve their overall cognitive function, illustrating the profound impact of water on mental well-being.
The Bottom Line
The signs of dehydration extend beyond mere thirst, encompassing a range of physical and mental symptoms that can significantly impact health and well-being. From the discomfort of dry mouth and skin to the more severe implications of rapid heart rate and cognitive changes, the body provides clear signals when it requires hydration. Recognizing and responding to these signs is crucial for maintaining optimal health, emphasizing the importance of regular water intake as a fundamental aspect of daily self-care. By staying vigilant about hydration, individuals can support their body’s functions, prevent dehydration’s adverse effects, and promote a healthy, vibrant life. Let this article serve as a reminder of water’s vital role in our health and the importance of listening to our body’s needs, ensuring we stay hydrated and thrive.


