Air pollution, a critical environmental issue, poses a significant threat to human health and well-being. With industrialization and urbanization on the rise, pollutants released into the air have reached alarming levels, impacting populations worldwide. Understanding how air pollution affects our health is crucial in combating its detrimental effects. This article delves into the ways air pollution can shorten your lifespan, highlighting the immediate and long-term health consequences, the mechanisms of damage, and the populations most at risk. By the end, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of why tackling air pollution is essential for a healthier future.
Contents
Understanding Air Pollution

Air pollution refers to the presence of harmful substances in the atmosphere, which can come from both natural and human-made sources. These pollutants include particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Industrial activities, vehicular emissions, household pollutants, and natural occurrences such as wildfires contribute significantly to the pollution levels. According to the World Health Organization, around 91% of the world’s population lives in places where air quality levels exceed WHO limits.
The complexity of air pollution lies in its varied sources and types. Particulate matter, for instance, is composed of tiny particles that can penetrate deep into the lungs, while gases like sulfur dioxide can cause immediate respiratory distress. The sources of these pollutants are diverse, ranging from factories and power plants to cars and household heating. Natural sources, such as volcanic eruptions and dust storms, also play a role, though human activities remain the primary contributors. Understanding the types and sources of air pollution is the first step in recognizing its impact on health.
Immediate Health Effects of Air Pollution
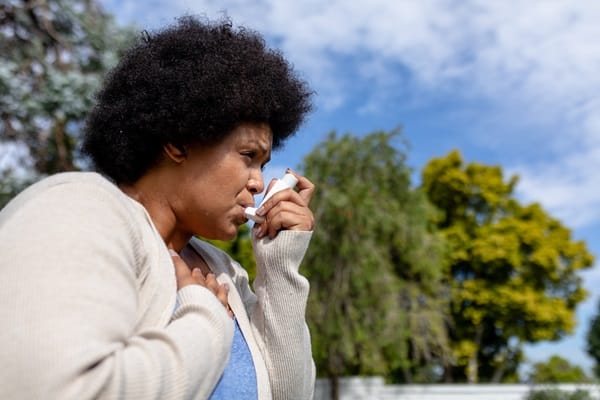

The immediate health effects of air pollution are most noticeable in the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. Short-term exposure can lead to respiratory issues such as asthma attacks, bronchitis, and other breathing difficulties. Those with pre-existing respiratory conditions are especially vulnerable, as pollutants can exacerbate their symptoms. Additionally, air pollution can cause irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat, leading to discomfort and potential secondary infections.
Beyond the respiratory system, air pollution can also have acute effects on the cardiovascular system. Short-term exposure to high pollution levels has been linked to increased heart rates and elevated blood pressure, which can strain the heart. In severe cases, this can lead to heart attacks or strokes, particularly in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions. Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly and children, are at higher risk of experiencing these immediate health effects, underscoring the urgent need for measures to reduce air pollution.
Long-Term Health Consequences
Long-term exposure to air pollution can lead to chronic respiratory diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer. The continuous inhalation of polluted air damages the respiratory tract, leading to inflammation, reduced lung function, and an increased risk of infections. Over time, these conditions can significantly impair an individual’s quality of life and, in severe cases, can be fatal. Studies have shown that people living in highly polluted areas are more likely to develop these chronic conditions compared to those in cleaner environments.
Air pollution also has profound effects on the cardiovascular system over the long term. Prolonged exposure to pollutants like particulate matter and nitrogen oxides can lead to the development of cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension, coronary artery disease, and even heart failure. Additionally, there is emerging evidence linking air pollution to other serious health issues, including diabetes and cognitive decline. The cumulative impact of air pollution on health can reduce life expectancy by several years, emphasizing the critical need for sustained efforts to improve air quality globally.
Mechanisms of Damage

Air pollutants enter the body primarily through inhalation, where they penetrate the respiratory system and sometimes even reach the bloodstream. Particulate matter, especially fine particles like PM2.5, can bypass the body’s natural defense mechanisms and embed deep within the lungs. These particles cause inflammation and oxidative stress, damaging lung tissue and impairing respiratory function. Over time, the accumulation of these particles can lead to chronic respiratory diseases and reduced lung capacity.
The biological processes affected by air pollution extend beyond the respiratory system. Pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide can trigger systemic inflammation and oxidative stress, which have widespread effects on the body. These pollutants can damage blood vessels, leading to cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, heart attacks, and strokes. Furthermore, certain air pollutants can cause genetic mutations and cellular damage, increasing the risk of cancers and other serious health conditions. Understanding these mechanisms highlights the pervasive impact of air pollution on overall health.
Studies and Statistics

Numerous studies have established a clear link between air pollution and reduced lifespan. Research published in prestigious journals, such as The Lancet and the New England Journal of Medicine, has demonstrated that long-term exposure to high levels of air pollution is associated with increased mortality rates. For example, a landmark study by the Harvard School of Public Health found that every 10 micrograms per cubic meter increase in PM2.5 was associated with a 6% increase in the risk of death. These findings underscore the significant impact of air pollution on public health.
Statistical data further reinforces the severity of the issue. According to the World Health Organization, air pollution is responsible for approximately 7 million premature deaths annually. In highly polluted cities like Delhi and Beijing, residents have a significantly shorter life expectancy compared to those in cleaner areas. Case studies from these regions reveal a stark contrast in health outcomes, with higher rates of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases among the population. These statistics highlight the urgent need for effective policies and interventions to reduce air pollution and protect public health.
Vulnerable Populations

Certain groups are more affected by air pollution due to factors such as age, health status, and socio-economic conditions. Children, for example, are particularly vulnerable because their lungs are still developing, and they breathe more air per body weight compared to adults. Exposure to polluted air during childhood can lead to long-term health issues, including impaired lung development and increased susceptibility to respiratory infections. Similarly, the elderly are at higher risk due to age-related decline in lung function and the presence of chronic health conditions.
Geographic disparities also play a significant role in the impact of air pollution. Urban areas, especially in developing countries, tend to have higher pollution levels due to industrial activities and dense traffic. People living in these regions often face greater health risks compared to those in rural areas with cleaner air. Additionally, socio-economic factors can exacerbate the effects of air pollution. Lower-income communities may lack access to healthcare and live in areas with higher pollution levels, making them more susceptible to its harmful effects. Addressing these disparities is crucial for protecting vulnerable populations and ensuring equitable health outcomes.
Mitigation and Prevention Strategies

Individuals can take several personal measures to reduce their exposure to air pollution and protect their health. Using air purifiers at home can significantly improve indoor air quality by removing harmful particles and gasses. When pollution levels are high, it is advisable to limit outdoor activities, especially strenuous exercises that increase breathing rates. Wearing masks designed to filter out pollutants can also provide an additional layer of protection when venturing outside.
On a broader scale, community and governmental actions are essential for effective air pollution mitigation. Implementing and enforcing stricter emissions regulations for industries and vehicles can significantly reduce the release of harmful pollutants. Developing and promoting public transportation systems can decrease the number of private vehicles on the road, thereby lowering traffic-related emissions. Urban planning initiatives, such as creating green spaces and promoting the use of renewable energy sources, can also contribute to improved air quality. Global initiatives and agreements, like the Paris Agreement, play a critical role in coordinating international efforts to tackle air pollution and its impacts.
A Call to Action for Cleaner Air
Addressing the issue of air pollution is crucial for safeguarding public health and extending lifespans. The evidence linking air pollution to serious health consequences is compelling, highlighting the need for immediate and sustained action. By understanding the mechanisms of damage and identifying vulnerable populations, effective strategies can be developed to mitigate these risks. Both individual efforts and collective actions at community and governmental levels are essential. Implementing stricter regulations, promoting cleaner technologies, and fostering global cooperation can pave the way for a healthier, pollution-free future, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for everyone.


