Heart health is a subject that increasingly garners attention due to the soaring rates of heart-related illnesses globally. Managing heart health is not merely a concern for the elderly or those already afflicted with heart disease; it’s a proactive measure everyone should take. With the modern lifestyle comprising poor dietary choices, sedentary habits, and constant stress, the heart is often subjected to immense strain. This article aims to be an actionable guide in helping you lower your risk of developing heart disease. With comprehensive sections ranging from understanding the condition to preventive measures, medical treatments, and the importance of community support, this guide seeks to provide a holistic approach to tackling heart disease.
Contents
Understanding Heart Disease

Heart disease is an umbrella term that encompasses various conditions affecting the heart and circulatory system. These range from coronary artery disease arrhythmia to congenital heart defects. The implications are grave, leading to impaired heart function, reduced blood flow, and potential organ failure.
To combat heart disease effectively, it’s crucial to grasp how it impacts the body. When this condition afflicts one, the heart can struggle to pump blood efficiently, affecting all organ systems. Over time, the persistent lack of adequate blood flow can lead to complications, including stroke, heart attack, and even death.
Know the Risk Factors

Risk factors for heart disease can be both genetic and lifestyle-based. While changing one’s genetic makeup is impossible, awareness of a family history of heart disease can lead to early intervention and management. Lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and a poor diet are additional risk factors that individuals can modify.
It’s also worth considering stress as a significant contributor to heart health. Elevated stress levels lead to the release of hormones that constrict blood vessels and raise blood pressure, providing a direct pathway to heart disease. Awareness of these risk factors can offer a strategic advantage in lowering heart disease risk.
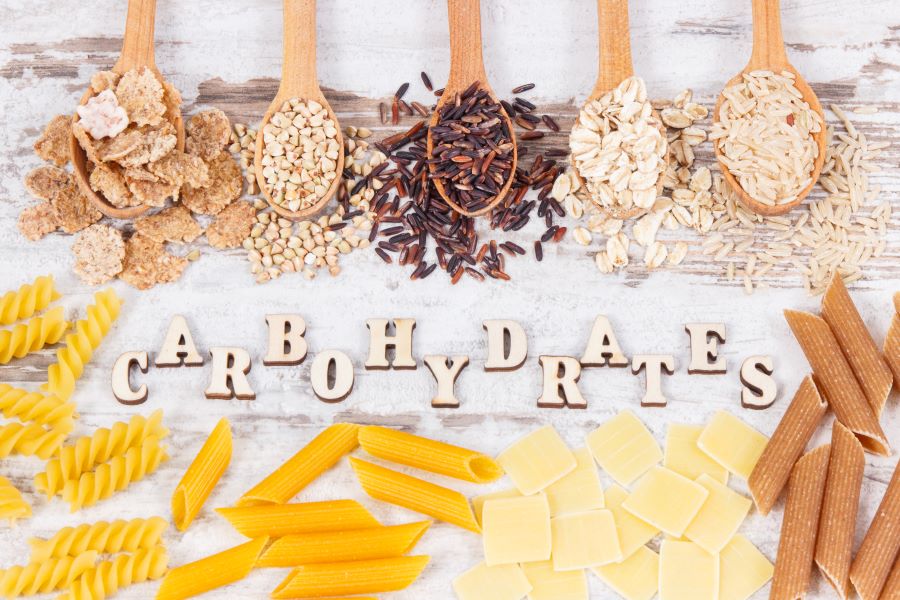
The Role of Diet

Diet plays a pivotal role in determining heart health. What is consumed directly impacts weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels—all factors intricately linked with heart disease. Saturated fats found in red meat and full-fat dairy products can contribute to arterial plaque buildup, eventually leading to heart attacks or strokes.
Fortunately, dietary changes can lead to significant improvements in heart health. A heart-friendly diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish such as salmon and mackerel, have shown beneficial effects in reducing heart disease risk. Incorporating such foods into one’s diet can significantly reduce the chances of developing heart problems.
Exercise and Physical Activity

Regular physical activity is paramount when it comes to maintaining a healthy heart. Exercise improves cardiovascular efficiency, lowers blood pressure, and helps manage weight, reducing the risk of developing heart disease. Cardiovascular exercises like running, swimming, and cycling are highly effective, elevating the heart rate and improving blood circulation.
Strength training, often overlooked in the context of heart health, is also beneficial. It helps build lean muscle mass, which boosts metabolic rate and aids in weight management. A combination of both cardiovascular and strength training exercises ensures that the heart and the circulatory system remain in optimal condition.
Stress Management Techniques
Excessive stress harms heart health, leading to increased blood pressure and the release of stress hormones that could harm the circulatory system. It becomes crucial to manage stress effectively to keep heart disease at bay. Techniques such as mindfulness and meditation have shown promise in reducing stress and improving overall well-being.
Another useful stress management strategy is controlled breathing exercises. Slow, deliberate breaths can help lower blood pressure and heart rate, offering immediate relief during stressful situations. Consistent application of these techniques can go a long way in ensuring a healthier, more resilient heart.
Medical Check-ups and Screenings

Regular medical check-ups are a preventative measure against the onset of heart disease. Routine blood pressure monitoring and cholesterol checks can offer valuable insights into heart health. Moreover, these check-ups can help identify risk factors or early signs of heart issues, allowing for timely intervention.
The frequency of these screenings varies from person to person, depending on age, family history, and existing medical conditions. Generally, yearly check-ups are advisable for most adults. However, those at higher risk may require more frequent tests to closely monitor their heart health.
Medication and Treatment Options

Medication is necessary for some individuals to manage heart disease risk. Drugs like statins are often prescribed to manage high cholesterol levels, while antihypertensives help control high blood pressure. Both types of medication can significantly reduce the risk of heart complications when used appropriately.
Adherence to medication regimens is crucial for their efficacy. Discontinuing medication or altering doses without medical advice can adversely affect heart health. It’s important to consult healthcare professionals for personalized treatment plans, and to stick to them rigorously.
Community and Support
Support from friends and family can profoundly impact one’s journey towards better heart health. A supportive environment encourages healthy lifestyle choices and offers emotional sustenance, which is vital for long-term success. A supportive community can make the task less daunting, from workout buddies to shared family meals featuring heart-healthy recipes.
Beyond the immediate circle of friends and family, numerous support groups and educational resources are available. These platforms offer additional guidance and emotional support, often proving invaluable in maintaining focus and resolve in adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle.
The Bottom Line
Heart disease remains a formidable adversary, but it can often be countered with informed proactive measures. From understanding the condition and its risk factors to adopting a balanced diet, regular exercise, and effective stress management techniques, there are various ways to reduce the risk of developing heart disease. Regular medical check-ups and adherence to prescribed medications supplement these lifestyle changes, offering a multi-pronged defense against this pervasive condition. The journey to better heart health is continuous, necessitating persistent effort and community support. However, the rewards—increased longevity, improved quality of life, and peace of mind—are worth the effort. Therefore, the call to action is clear: take charge of your heart health today for a better tomorrow.


